Sponsored content 2: the game
- Sponsored content
- Advertising that a brand pays an online publisher to create and seamlessly integrate, conforming to the design, format, and content of the website or social media feed where it is published. Dictionary.com
In this lesson, the students take part in an interactive exercise that helps them learn how to recognize sponsored content.
Lesson goals
- Critical thinking
- Information literacy
Activities
Exercise (45 minutes) - Group work
The students perform the exercise in smaller groups.
Aim: the students practice their skills of recognition of sponsored content.
Presenting (25 minutes) - class
The students report their findings to each other.
Aim: the students communicate their findings to each other.
Discussion (20 minutes) - Class
The students discuss their findings.
Aim: the students reflect on what they have practiced.
Pedagogical tips and recommendations
- This exercise is easier if there is at least one computer available per group, but smartphones will suffice.
Exercise (45 minutes)
Split the class into groups (up to 5 members). The objective of the exercise is simple. Each group will decide on a platform/type of media to work on and look for examples of sponsored content. They should try to find examples of all the different types of sponsored content: regular advertisements, product placement, native ads, and sponsored reviews.
Sample delegation of roles:
- Group 1: Instagram
- Group 2: Large traditional news media of the nation
- Group 3: Blogs
- Group 4: YouTube
- Group 5: Smaller and local media
Step 1 (10 minutes)
Groups browse through content on the platform they are assigned and looking for content that is likely sponsored. They are also allowed to include content they are not sure about. During this time, the teacher should observe the students and offer help if necessary.
Examples of different types of sponsored content:
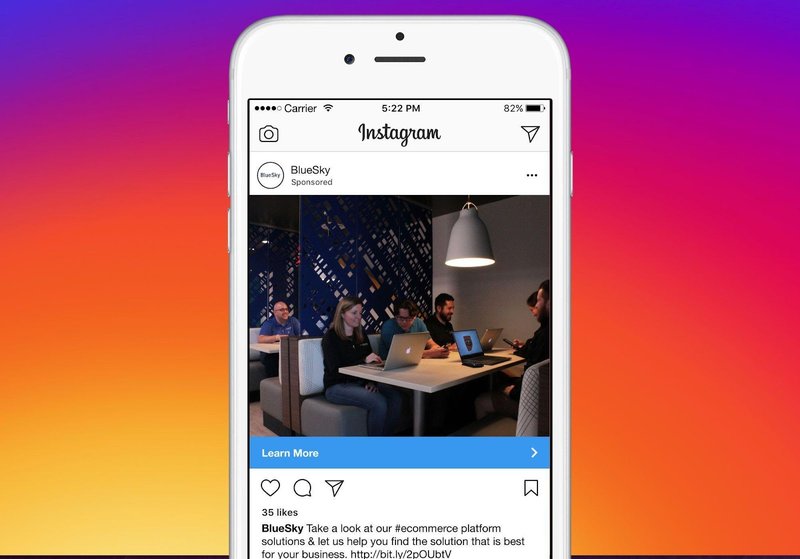
Regular advertisement: example of an Instagram post that seems like any other post but is, however, sponsored. This could be called native advertisement too. However, it is a bit more distinguishable.
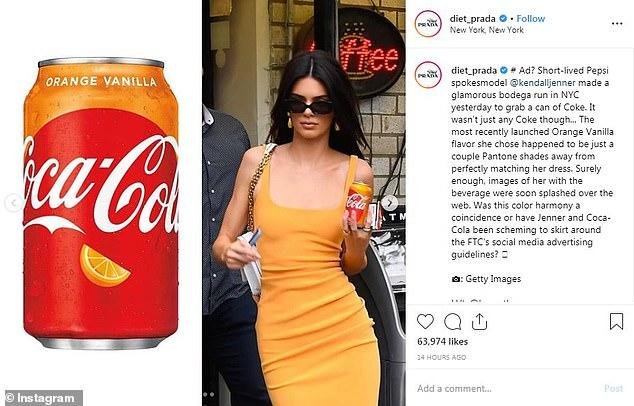
Product placement: example of an (alleged) situation where an influencer dressed in the colors of a new Coca-Cola flavor in an attempt to blend with the product (and take pictures with it inadvertently).
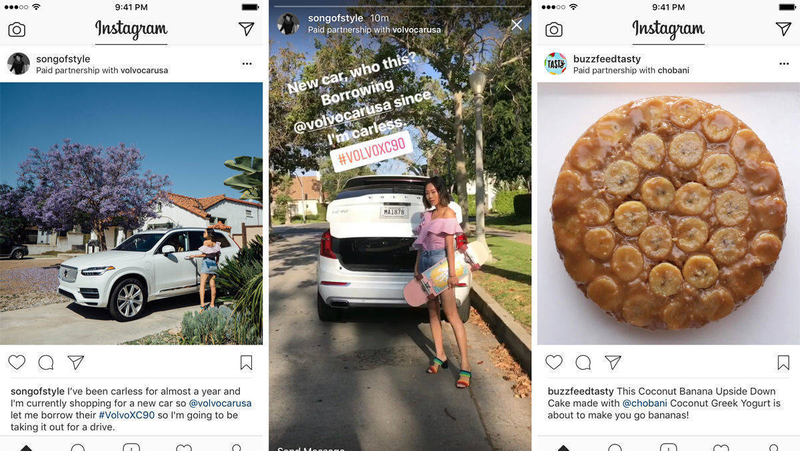
Native ads: These ads all seem like just another post, even though they are, in fact, sponsored. In this case, Instagram lets you know that a paid partnership exists, but this can be less clear in other examples.
Sponsored review: this is an example of a review, that is clearly sponsored, however, that fact is, in this case, relatively clear.

Step 2 (20 minutes)
After identifying their examples, students should brainstorm and develop a clear concept for each of the examples they found. This involves
- identifying the type of sponsored content,
- identifying the target audience, and
- the purpose of each piece of sponsored content.
Step 3 (10 minutes)
At this point, students should connect their examples to the type of media they have been assigned and discuss within the group how the medium through which they are broadcast influences the sponsored content itself.
Step 4 (5 minutes)
The students should prepare to present their findings to the rest of the class.
Presenting (25 minutes)
Each group presents their findings to the rest of the class. The rest of the students and the teacher can ask questions to the group presenting. The questions at this point should be more technical, for example:
- How do you know this content is sponsored?
- Why did you categorize this content like so?
Discussion (20 minutes)
- Was there more or less sponsored content than you thought?
- How does the type of media influence sponsored content?
- Why do you think companies choose to create sponsored content instead of traditional advertisements? What advantages does sponsored content offer?
- Do you think it is possible for you to have missed any sponsored content?
- What does one need to be able to recognize sponsored content?
- Would you ban sponsored content? Maybe solve the issue some other way?
- What role does critical thinking play in protecting consumers from potentially harmful or deceptive sponsored content?
- How can individuals become more savvy media consumers?